Wall Street Journal: Why It’s Time To Buy Homes
Wall Street Journal | WEEKEND INVESTOR | JUNE 4, 2011
Why It’s Time To Buy
The Clouds Haven’t Quite Parted, But the Long-Term Case for Home Ownership Is Looking Stronger
By RUTH SIMON and JESSICA SILVER-GREENBERG
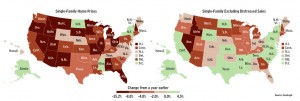
Back in June 2006, when the housing market peaked, the prospect of a five-year national housing bust seemed unimaginable to most people. And yet here we are, with the latest Standard & Poor’s Case-Shiller index showing that prices hit new bear-market lows, falling back to 2002 levels nationally and to 1990s levels in some battered regions.
Such conditions might not last long. Moody’s Analytics predicts that the number of distressed sales will begin to fall in 2013, and that prices will begin to edge upward then. Home building is at a virtual standstill, so the supply overhang isn’t likely to get much worse. Meanwhile, demographic indicators such as “household formation”—the number of new households each year—are on the rise, and promise to take a bite out of the glut in coming years.
The upshot: “While we might not see rapid growth in the next couple of years, there are a tremendous number of positive signs that could lead to a rebound,” says Anthony Sanders, a real-estate finance professor at George Mason University.
…
Demographics
Household formation fell during the economic downturn as a weak economy led some people to stay in school, double up with roommates or move in with family members. According to Moody’s Analytics, the number of new households renting or owning a home dropped to 578,000 in 2008 from nearly 2 million in 2005, just before the peak of the housing boom.
But household formation increased to nearly 950,000 last year, says Moody’s, and should average 1.2 million over the next decade. That, combined with increased obsolescence and higher demand for second homes, should begin sopping up excess inventory in much of the country over the next two years, Moody’s says. “Whatever the excess supply of housing is, it is shrinking pretty fast,” says Thomas Lawler, an independent housing economist.
…
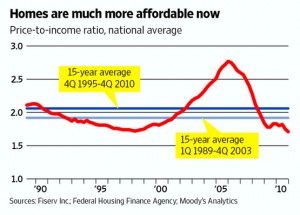
AffordabilityRising home prices made renting cheaper than buying in many parts of the country. But that dynamic has begun to change: Housing affordability, as measured by the ratio of median home prices to median household incomes, has fallen below pre-housing bubble levels in just over two-thirds of the country, according to an analysis of more than 380 metro areas by Moody’s Analytics.
Renting is still cheaper than buying in most markets, but rising rents and falling house prices mean that, in some areas, this won’t be the case for long. Buying a home is already cheaper than renting in Chicago, Cleveland, Detroit and Orlando, Fla., according to Moody’s Analytics. In other markets, including Dallas, Las Vegas and Sacramento, Cailf., the equation is likely to soon turn in favor of homeownership if current trends persist, the firm says.
…
Employment
The strength of the housing market depends largely on the economy. Rising incomes and increased employment tend to give more would-be buyers confidence and buying power. For now, job growth remains sluggish: On Friday the Labor Department reported that just 54,000 jobs were created in May, far below expectations.
But signs of how a stronger job market could fuel housing demand are evident in the Dallas metro area, which added 83,100 new jobs in the 12 months ending in April—the largest gain in the nation, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Dallas never had a big housing boom or bust and has benefited from trade with Mexico, a strong telecommunications sector and a central location.
…
Credit
Mortgage financing remains plentiful for borrowers with good credit scores and solid employment histories. But for borrowers who don’t fit traditional lending standards, getting a loan can still be nearly impossible. In the first quarter, about 10% of banks tightened standards for nontraditional loans, according to the Federal Reserve. Meanwhile, higher down-payment standards are locking some would-be buyers out of the market. Just 35% of renters have the minimum 3.5% down payment needed for an FHA loan on the median-priced home in their market, according to a recent survey by Zelman Associates.
Credit is likely to remain tight for at least the next six months, says Clifford Rossi, a former Citigroup Inc. consumer-lending executive who teaches at the University of Maryland.
But conditions should improve over time, he says: “There’s no question that it will gradually get easier.”
…
Psychology
The long-term case for buying over renting remains in force. Yet nowadays, “People are simply scared,” says Aaron Galvin, chief executive of Luxury Living Chicago, which finds rental apartments for wealthy clients.
Mr. Galvin says he has seen a 30% increase in business in the last year, driven by would-be home buyers who can afford to purchase a property but are choosing not to do so.
The portion of Americans who believe homeownership is a safe investment dropped to 66% in the first quarter from 83% in 2006, according to Fannie Mae, the government-controlled mortgage company.
…